

The essence of NovelEdge™
Technology is the ability to utilize a great deal of supplemental
firing to add low cost capacity, only without the detrimental effects
on heat rate that is prevalent in the conventional combined cycle.
To accomplish this task, a unique heat recovery method, in conjunction
with a more efficient bottoming cycle is employed.
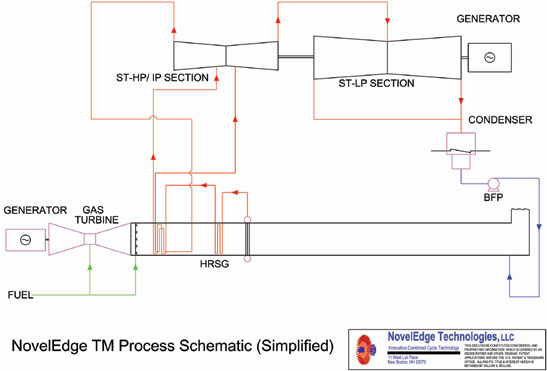
The process schematic below illustrates a high-efficiency conventional
combined cycle plant that is typical in the industry. This cycle
utilizes a gas turbine, 3 pressure level HRSG, and a reheat steam
turbine. Design point HRSG stack temperatures are normally in
the 180 to 220 F range. The steam turbine typically provides 30
to 50% of the overall plant capacity (a steam turbine to gas turbine
capacity ratio of 0.43 to 1.0).

The NovelEdge™ Technology
process schematic is similar to the conventional combined cycle
plant in that it utilizes a gas turbine, an HRSG, and a reheat steam
turbine. In addition, design point HRSG stack temperatures are normally
in the 180 to 220 F range. However, the NovelEdge™
Technology HRSG has only one high-pressure drum, versus 3 pressure
levels in the conventional plant. The steam turbine is much larger
and does not require admissions for IP and LP steam. And the amount
of supplemental firing is not as limited as in the conventional
plant, as there is no worry concerning boil-out in the IP section.
For the NovelEdge™ Technology
process, the steam turbine typically provides 50 to 70% of the overall
plant capacity (a steam turbine to gas turbine capacity ratio of
1.0 to 2.3).
EPC contractors, developers, and independent consultants have verified
the performance for this technology. In addition, it has been modeled
on GateCycleTM, from GE Enter Software.
The NovelEdge™ Technology
schematic shown here is in simplified form. For a more detailed
process schematic, along with a process description and performance
runs utilizing GateCycle, please contact
us.
|

